Stretch Goal Reports
Glossary Words from the following Reports: Working Age
Report: Interprovincial Migration

Report: International Immigration

Summary Report
Importance
- Growing New Brunswick's population base is key to:
- Improvng the economy
- Developing communities
- Meeting employment needs
- Correcting population demographics
- Increasing the population will stimulate economic development and attract private sector investment
- This can be done through international immigration, interprovincial immigration, or increased birth rates relative to mortality rates
Problem
- New Brunswick’s population share is shrinking due to an aging population and poor retention of youth and immigrants
- In 1976, New Brunswick’s population share peaked at 2.94%; however, it has since dropped by 30%, reaching 2.06% in 2021
- Annual growth that matched the national rate would maintain NB’s population share and boost its economy
Cause
- New Brunswick’s low population growth rate can be seen as the result of several factors
- An imbalance between the aging population and youth population
- Low fertility rates – too few births – have caused New Brunswick’s death rates to exceed its birth rates every year since 2015
- Youth leaving New Brunswick in search of employment has also put negative pressure on the province’s population share
- These factors can be offset by net positive migration and attracting young people to the province
- See BoostNB’s goals on Interprovincial Migration and International Immigration
In The Numbers
Over the past 50 years New Brunswick has not been keeping up with the national population growth rates, leading to a shrinking population share and an aging demographic putting stress on the New Brunswick economy. Between 2000 and 2015 New Brunswick frequently experienced negative growth rates but has since averaged growth around 1%, and from Q2 2021 to Q2 2022 experienced growth 0.5% better than the national rate. This was due to a large influx of interprovincial immigrants in New Brunswick and low international immigration in the nation as a whole. It is not clear if this should be expected to be immediately repeatable.
Figure 1: Population Growth Rates
Sources of Growth
Historically, most of New Brunswick’s population growth came from natural increase – birth rates exceeding mortality rates. However, with an increasingly aging demographic and decreasing fertility rates the province’s natural population change has been decreasing since the 1970’s and has been negative since 2015. This demographic problem can only be corrected by immigration of young people. Since 2014, immigration both international and interprovincial has been increasing but has not yet been able to consistently match the national rates of population growth.
Figure 2: Sources of Population Change
Natural Change
Due to the aging population and outmigration of young people from New Brunswick, there is a clear and consistent decline in the natural increase, which is births minus deaths in the provinces. This is driven both by an increase in deaths and a larger decrease in births in the province as seen in Figure 3. To reverse this trend, it will be necessary to bring young people into the province through migration. In 2015 the death rate exceeded the birth rate for the first time, leading to a natural decrease.
Figure 3: Components of Natural Change
Summary
New Brunswick’s population share is declining due to an aging population and poor retention of
its younger population. Increasing the province's population share could stimulate economic growth.
This could be accomplished by receiving a larger number of working age immigrants from across Canada or internationally.
International immigration has shown progress over a twenty-year period, but recent data
shows a sharp drop in 2021. Fortunately, much of this slack has been made up by interprovincial migration.
Since New Brunswick’s historic levels of inter-provincial migration losses in 2014, the province has steadily improved
its position and reached the goal in each of the previous three years. It remains to be seen whether this strong performance
will continue through the Covid-19 recovery period, but the positive trend since 2014 coupled with the fact that New Brunswick
has reached this goal in consecutive years are reasons for optimism.
The attracting and retaining of skilled young people will be vital to New Brunswick’s economic growth going forward,
this will have an immediate impact not only on population but also on natural growth rates which have been falling for at
least a half century.
Appendix
Appendix A: Population Growth Rate
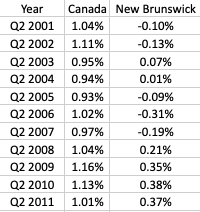
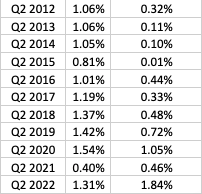
Source: Statistics Canada. Table 17-10-0008-01 Estimates of the components of demographic growth, annual. DOI: https://doi.org/10.25318/1710000801-eng.
Appendix B: Sources of Population Growth
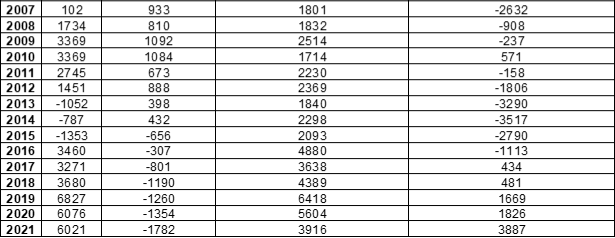
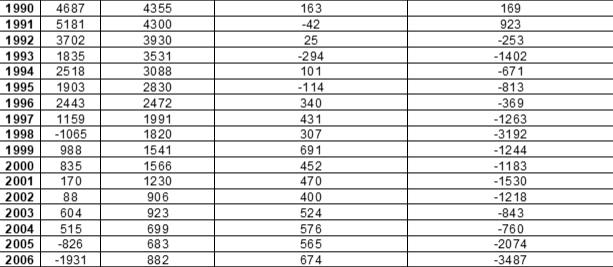
Source: Statistics Canada. Table 17-10-0008-01 Estimates of the components of demographic growth, annual. DOI: https://doi.org/10.25318/1710000801-eng





